EDIT 2020-09-28T22:00:00Z: there is a more recent version of this article here Understand How to Build a Firmware and its Dependencies — MicroEJ Documentation
In the following post, we assume:
- MicroEJ SDK 4.x is installed with an activated license (evaluation license or production license).
- The reader is familiar with the MicroEJ glossary MicroEJ Glossary — MicroEJ Documentation.
- The reader has run one of the MicroEJ SDK getting started Get Started - Create Apps and Build a VEE Port - MicroEJ Technology.
- The reader has access to the MicroEJ SDK developer guide (pdf, see on developer.microej.com → guide).
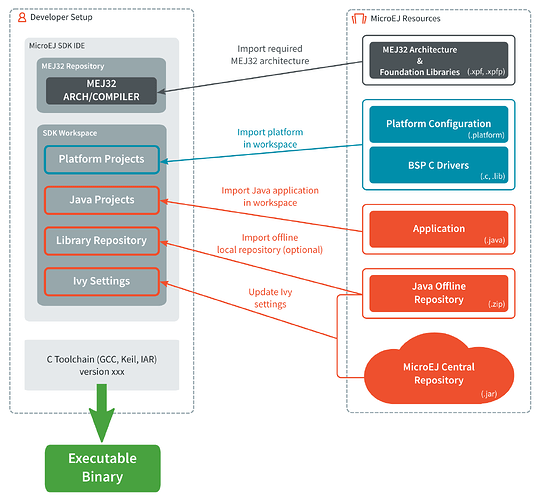
A MicroEJ firmware is built from several input resources and tools. Each resource and tool has a specific version that must be carefully respected in order to build a firmware.
-
The MicroEJ SDK IDE [.exe or .zip].
-
A MEJ32 architecture [.xpf, .xpfp]: the runtime port to a target instruction set (ISA) and a C compiler (CC) and MicroEJ Foundation Libraries.
- The MEJ32 architectures are distributed into 2 formats:
- EVAL: evaluation license with runtime limitations (explained in SDK developer guide).
- DEV: production license (these versions are only distributed by MicroEJ sales & Customer Care team).
- The list of supported MEJ32 architectures can be found here MicroEJ Developer - Embedded Runtime Architectures & Implementations. - The MEJ32 architecture is either provided from:
- the
/platformArchitecturefolder in a MicroEJ platform reference implementation (downloaded from https://developer.microej.com/). - MicroEJ sales or customer care team.
- For DEV license only: SDK license site https://license.microej.com/ (MyProduct->Download additional products will list the downloads available for your account).
- the
- Must be imported in SDK with:
-
File→Import… -
MicroEJ→Platform, Virtual devices and Architectures -
Select directory→Browse…, choosex/platformArchitecture/>OK - Accept the license (Check the
I agree...box) -
Finish.
-
- The MEJ32 architectures are distributed into 2 formats:
-
A MicroEJ platform source (.zip).
- This package includes:
- the build of a C board support package (BSP, with or without RTOS),
- a MEJ32 Architecture,
- the adaptation layers (ADLAs),
- the MicroEJ Simulator and its associated MicroEJ Mocks.
- The zip files contains:
-
<platform>-configuration: The configuration of the MicroEJ Platform -
<platform>-bsp: The C code for the board-specific files (drivers).
Must be compiled with a compiler. -
<platform>-fp: Front panel mockup for the simulator.
-
To generate the platform:
- In the
<platform>-configuration:
open the.platformfile and verify the correct MEJ32 architecture is used
(seeContentview). - Click on
Build Platform.
This action generates a<platform>-<ISA>-<CC>-<VERSION>folder that contains the platform runtime library (microejruntime.lib).
This library is usually directly linked from the<platform>-bspproject (no manual action to do after the build). - Follow the README instructions inside the platform .zip.
- This package includes:
-
A Java application project (.zip).
This Java project can be configured (in theRun configurations ...properties):- to either run on:
- a simulator (computer desktop),
- a device (actual embedded hardware).
- to setup:
- memory (example: Java heap, Java stack),
- foundation libraries,
- etc…
This project is compiled against (and optimized for) a specific MicroEJ SDK platform:
- Generates a
microejapp.o(native object code) that is usually directly linked from the<platform>-bspproject (no manual action to do after the build). - Go in:
-
Run→Run configurations - select the provided
MicroEJ Applicationlaunchers - click on
Run
-
- Must be imported in SDK with:
File>Import…>General>Existing Projects into Workspace>Select archive file>Browse…, choosex.zipandFinishimport.
- to either run on:
-
An Ivy repository.
- MicroEJ Central Repository: an online repository of software artifacts (libraries, tools, …), see https://repository.microej.com/.
- (Optional) Can be extended with an offline repository (.zip) that can be imported in the workspace:
- Unzip the
x-repository-M.m.p.zipfile. - Open MicroEJ SDK.
- Go to
Window > Preferences > Ivy > Settings. - Configure the
Ivy settings pathby clicking theFile System...button. - Select the
ivysettings.xmlfile available in the directory where you have previously unzipped thex-repository-M.m.p.zipfile.
- Unzip the
-
A C compiler (GCC, KEIL, IAR, …).
- Used to compile and link the following files into the final firmware (binary, hex, elf, … that will be programmed on the hardware):
- the
microejapp.o(application), - the
microejruntime.libormicroejruntime.a(platform), - the BSP C files (drivers).
- the
- Used to compile and link the following files into the final firmware (binary, hex, elf, … that will be programmed on the hardware):
Support
If any questions, feel free to contact our support team with the following information (the table below is filled with examples)
| Delivery | Name |
|---|---|
| MicroEJ SDK | 4.1.5 |
| MEJ32 XPF | ARM Cortex-M / KEIL DEV |
| Platform | 1.0.0 |
| Application | 1.0.0 |
| Ivy Repository | https://repository.microej.com/packages/repository/1.10.0/microej-4.1-1.10.0.zip |
| C compiler | KEIL 5.25 |